Contents
What is IELTS
IELTS cost
IELTS dates
IELTS registration
IELTS preparation
IELTS test format
IELTS listening
IELTS speaking
IELTS reading
IELTS writing
What is IELTS ?
IELTS is an abbreviation. It stands for International English Language Testing System.
IELTS is an English exam organised jointly by the British Council, Cambridge English Language Assessment and IDP Education Australia. The exam measures students’ level of proficiency in the English language. Students are given an overall band score between 1 (non-user) and 9 (expert).
Many organisations use the IELTS exam as a condition of entry into their organisation. That is why the exam is so valuable. The IELTS certificate is accepted by over 8000 organisations (universities, companies, governments) from 135 countries all over the world, including over 3,000 institutions and programs in the USA. All of the Top 25 US universities accepting foreign students accept IELTS as proof of English proficiency.
More than 2 million people take the test every year.
There are 2 versions of the test and the choice depends on the organisation you are applying to and your reasons for taking the test:
IELTS Academic – For students who want to study at an English-speaking university or educational institution.
IELTS General Training – IELTS General Training measures English language proficiency in a practical, everyday context. The tasks and texts reflect both workplace and social situations. General Training is suitable for immigration purposes to Australia, Canada, New Zealand and the United Kingdom.
Both versions give a band score of 1 to 9 and test the 4 skills reading, writing, speaking and listening. The format of the test is however slightly different.
IELTS cost
The exact cost of the IELTS depends on where you take it. Here is a guide of the approximate test fee by location:
UK: £160
Western Europe: Between € 220 and € 230
USA: Between $215 and $240
Brazil: R$ 800
Canada: CAD 309 (depending on the test centre)
China: RMB 1,960
India: INR 11,800
Indonesia: IDR 2,900,000
Philippines: Php 10,270
Russia: RUB 15,000 – RUB 24,000 (depending on the test centre)
For the exact price, choose your test location
IELTS dates
The IELTS exam is organised at test centres all over the world. The IELTS Academic exam is organised on 48 dates during the year (four tests per month ) and the IELTS General Training exam is organised on 24 dates during the year (two tests per month.)
IELTS registration
If you aren’t sure how to register for the IELTS exam, then rest assured the process is quite simple:
1) Find your nearest test centre
2) Register online directly and pay online. Or alternatively, you can download an application form , fill it in and send it to your test centre.
After registration, you will receive confirmation of the booking by post or email with all the instructions for your exam day.
Full instructions for how to book your place are available here on the IELTS website.
IELTS test format
The IELTS test assesses your abilities in 4 skills: listening, reading, writing and speaking. The total test time is 2 hours 45 minutes.
Listening and Speaking are the same for the Academic and General Training tests. However, the reading and writing parts are different depending on which test you take. (More details below)
The listening, reading and writing tests are done in the test centre on the same day. For the speaking test, it depends on the test centre. – Sometimes it will be on the same day as the rest of the test and sometimes it will be separate, a few days before. Your test centre will be able to confirm this for you.
IELTS listening
The listening test is made up of 4 sections. Each section has 10 questions so that makes a total of 40 questions. Each question is worth one mark for a toal of 40 marks for the listening test as a whole.
The questions appear in the same order as the spoken words in the audio recording. In other words, you will hear the answer to question 1 before you hear the answer to question 2. The last answer you hear will be the answer to question 10.
The audio recordings are played one time only. They can contain different types of English accents (British, American, Australian, Canadian, New Zealand)
Section 1
This is a conversation between 2 people. They will be discussing an everyday social situation.
Section 2
In section 2, there is only one person speaking. This is usually a speech or presentation about an everyday social situation. Example, it could be a speech about a town.
Section 3
This is a conversation between 2 people. They will be talking about an educational or academic topic.
Section 4
In section 4, there is only one person speaking. It’s a monologue. This is usually a speech or presentation about an academic topic. Example, it could be a speech about welcoming students to the university.
During each section, you will write your answers on the question sheet because it is easier to write the answers quickly next to the questions. But before you hand in your answers, you must transfer those answers to the official answer sheet. You must therefore be very careful to correctly copy your answers over without making any spelling mistakes. Only answers on the answer sheet will be accepted. The actual listening time is approximately 30 minutes and you are given 10 minutes to transfer your answers to the answer sheets. The total allowed time is therefore 40 minutes.
There are several types of question in the listening test: multiple choice, matching, plan/map/diagram labelling, form/note/table/flow-chart/summary completion and sentence completion.
Here is a description of each type of question on the listening test with examples:
Multiple choice
In multiple choice questions, there is a question followed by 3 possible choices. (A, B or C) You must write the correct choice (A, B or C) on the answer sheet. There is only one correct choice.
Example:
Choose the correct letter A, B or C
The CEO will be in the office:
A on Monday morning only.
B all day Monday.
C all day Monday and Tuesday.
On certain multiple choice questions, there is a longer list of possible answers. There is more than one correct choice. Read the question very carefully to see how many correct choices there are. You must write the correct choices on the answer sheet.
Example:
Choose 2 letters A – E
Which two pieces of information does the doctor give about the blood tests?
A You must make an appointment.
B They are free.
C They are only for adults.
D They are taking place during the month of March.
E They are being done in public hospitals.
Matching
You are asked to match a list of items with another list of items based on information from the audio recording. Make sure you read the question very carefully. In particular pay attention to how many items you are being asked to match from the list.
Example:
What is the main area of work of each of the following people?
Choose FOUR answers from the box and write the correct letter A – G next to questions 1-4.
| A Marketing B Sales C Production D Accounts E Customer service F Human Resources G Training |
1 David …………………..
2 Sarah …………………..
3 Richard …………………..
4 Jane …………………..
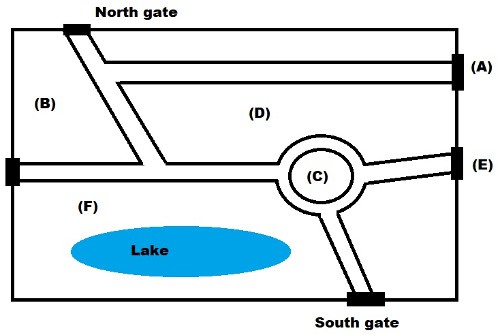
Plan, map, diagram labelling
You are asked to complete labels on a plan (example an architectural plan), map (example of part of a city) or diagram (e.g. of a process or object).
Example:
Questions 5-7
Label the map below. Write the correct letter A-F next to the questions 5-7
5 Entrance ………………………..
6 Flower garden ………………………..
7 Forest ………………………..
Form, note, table, flow-chart, summary completion
With this type of question, you are asked to complete the gaps in an outline of part or all of the listening text. An “outline” is a summary of the most important details of something.
The “outline” that you are asked to complete can be any one of the following formats:
Form: Example an application form
Set of notes: This is usually a summary of something in written format.
Table: A summary in table format with columns and rows.
Flow-chart: A diagram with boxes, text and arrows. The flow-chart represents a process with clearly-defined stages.
There are usually 2 different ways you will be asked to fill in the gaps:
1)You will be asked to choose your answers from a list on the question paper.
or
2) You will be asked to write the missing word or words. The word limit will be defined in the question. Example: “NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER” – Make sure you read and understand the word limit. You will not be tested on contracted words (example: We’re ) Hyphenated words (example pre-defined) count as ONE word.
You may have to select answers from a list on the question paper or identify the missing words from the recording, keeping to the word limit stated in the instructions. You do not have to change the words from the recording in any way.
Example:
Questions 15-20) Complete the table below. Write NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER for each answer.
| Hotel | Business facilities | Location |
| Park hotel | (16)______ rooms, fax and (17)______ | Close to (19)___________ |
| (15)______ travel inn | Free (18)_____, executive lounge | Only 500m from (20)___________ |
Sentence completion
In this type of question, there is a text made up of several sentences. The text is a summary of what you heard during the listening. In the text, there are some gaps which represent missing words. You will be asked to write the missing word or words. The word limit will be defined in the question. Example: “NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER” – Make sure you read and understand the word limit. You will not be tested on contracted words (example: They’ve) Hyphenated words (example follow-up) count as ONE word.
Example:
Questions 12-14
Complete the sentences below. Write ONE WORD ONLY for each answer.
12 Lore says that lecturers at English universities are ……………………… than lecturers in France.
13 She felt ……………………… for the first few weeks.
14 She was shocked at how ……………………… everything was.
Short answer questions
This type of question consists of a question related to the listening. You will be asked to write the answer as a word or several words. The word limit will be defined in the question. Example: “NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER” – Make sure you read and understand the word limit. You will not be tested on contracted words (example: I’d) Hyphenated words (example family-owned) count as ONE word.
Example:
Questions 1-3
Answer the questions below. Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER for each answer.
1 In the first semester, how often did Cendrine work in a pharmacy?
2 What was the hardest part of studying in England?
3 Where would Cendrine like to work next year?
IELTS speaking
The speaking test is an oral test between the candidate and an IELTS examiner. The duration is 11-14 minutes. The whole speaking test is recorded. The speaking exam is assessed according to 4 criteria: Fluency and coherence, lexical resource (vocabulary), grammar and pronunciation .
There are three parts to the speaking test:
Speaking part 1: Introduction and interview
The examiner will introduce himself to you and ask to see your ID (passport, identity card, driving license) so make sure you take it into the room with you. You will be told what official documents are accepted as ID at registration. After the identification process, the test will start. The examiner will ask you several questions regarding some common topics such as family, home, friends, hobbies, studies, work.
This is not really an interactive conversation because the questions are from a list of questions from a script. In other words, the examiner will not ask further questions based on your answers to previous questions. That is why you should make sure you give complete answers where possible.
The duration of part 1 is about 5 minutes.
Speaking part 2: Short talk
In part two, the examiner will give you a card. On the card is a topic to talk about. Below the topic is a list of 3-4 points that you should mention during your talk. These points are there as prompts and will help you come up with ideas of what aspects to talk about and how to structure the talk. The examiner will also give you a pencil and some paper to help you prepare. You will have 1 minute in total to prepare. You can consult the task card during the preparation. Note that you cannot choose your topic. You cannot ask the examiner to give you a different topic if you don’t like it.
After the one minute of preparation, the examiner will ask you to start your presentation. The time limit is 2 minutes. It is recommend you talk for between 1 minute 30 seconds and 2 minutes. You must not talk for more than 2 minutes. After 2 minutes, the examiner will interrupt you and stop your talk. During your talk, you may consult the original task card as well as the notes you made during your preparation. At the end of the 2 minute talk, the examiner will ask you one or two questions about the topic.
The total duration of part two is about 4 minutes including the preparation time.
The topics aren’t complicated. They do not require any knowledge in a specific area. They are topics that anyone could talk about because they are based on personal experiences from common situations.
Example speaking task 2 questions
Example 1:
Describe a businessman or woman you admire.
You should say:
Who they are and what they do
How they became successful
How you found out about them
And explain why you admire them
Example 2:
Describe a subject you enjoyed studying at school.
You should say:
When and where you started studying it
What lessons were like
What made the subject different from other subjects
And explain why you enjoyed the subject
Example 3:
Describe a job you have done.
You should say:
How you got the job
What the job involved
How long the job lasted
Describe how well you did the job
Speaking part 3: Discussion
In part 3, the examiner will ask you more questions about the topic from speaking part 2. This will result in an in-depth discussion about the topic between you and the examiner. You may be asked for your opinions, to talk about abstract ideas, to suggest solutions to problems, to make comparisons or predictions. Where appropriate, you will be expected to back up your opinions with evidence and to develop your answers.
The total duration of part 3 is 4–5 minutes.
Example speaking part 3 questions:
Do you think technology improves our lives?
Why do some people refuse to vaccinate their children?
What are some ways to save money?
What are the main economical problems in your country?
Do you think we’ll have pilotless planes in the next 10 years?
IELTS reading
As previously mentioned, the IELTS reading test is slightly different, depending on whether the candidate is taking the IELTS Academic or the IELTS General Training exam.
IELTS Academic reading
The exam is made up of 3 texts for you to read, followed by a set of questions for each text. The texts have approximately 700 words each. They are from newspapers or magazines and can be on a wide range of possible subjects. There are a total of 40 questions for the whole reading exam across all 3 texts. So that means each text will have 13-14 questions. Each question is worth 1 mark. The duration of the whole reading section is 60 minutes. You must fill in your answers on the special answer sheet. No extra time will be given for you to transfer answers to this sheet.
IELTS General Training reading
The exam is made up of 3 sections:
Section 1 “Social survival” – This section is made up of several short texts containing information of a practical nature. The purpose of this section is to test your skills in accurately retrieving factual information from sources such as signs, timetables, announcements, adverts and notices.
Section 2 “Workplace survival” – This section is made up of 2 texts with questions related to the workplace. Example sources are work memos, email messages, job descriptions, training manuals.
Section 3 “General reading” – This section has 1 long text taken from a magazine or newspaper and a set of questions. The
There are a total of 40 questions for the whole reading across all sections. Each question is worth 1 mark. The duration of the exam is 60 minutes.
Types of questions
There are several types of question in the reading test. The types of questions are the same for both the Academic and the General Training exam. Here is a description with examples of each type:
Multiple choice
In multiple choice questions, a question is asked and several choices are listed as possible answers. The possible answers are identified by a letter. You have to write the letter of the correct answer on the answer sheet.
There are 3 types of multiple choice question:
1) There are 4 choices (A, B, C or D) and you have to choose 1 best answer.
2) There are 5 choices (A, B, C, D or E) and you have to choose 2 best answers.
3) There are 7 choices (A, B, C, D, E, F or G) and you have to choose 3 best answers.
Sometimes the question is a sentence with a missing word and the answer is the correct missing word. Alternatively, the question is a complete question and you have to choose the best answer to that question among the available choices.
Example:
Question 24
Choose the correct letter A, B, C or D.
Write the correct letter in box 24 on the answer sheet.
According to the writer, the worst thing about living in New York is:
A The high cost of living.
B It’s hard to find true love.
C The cold weather.
D The city is very dangerous.
Identifying information
With this type of task, you are given a statement and you have to say if that statement is true or false based on the text. If there is no evidence to say if the statement is true or false, then you must reply with “not given”.
Example:
Questions 1-3
Do the following statements agree with the information in the reading passage?
In boxes 1-3 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if the statement agrees with the information
1 Mr Jones worked for Mrs Smith as a private detective.
2 Mrs Smith left school with no qualifications.
3 Mrs Jones was angry because she hadn’t been paid.
Identifying writer’s views/claims
You are given a statement and you have to say if that statement agrees with the views/claims of the writer based on the text. If there is no evidence to say if the statement agrees with the writer’s views or claims, then you must reply with “not given”.
Example:
Questions 8-10
Do the following statements agree with the claims of the writer in the reading passage?
In boxes 8-10 on your answer sheet, write
YES if the statement agrees with the claims of the writer
NO if the statement contradicts the claims of the writer
NOT GIVEN if it is impossible to say what the writer thinks about this.
8 Alcoholism is a disease.
9 Most people are too poor to eat healthily.
10 Positive thinking helps cure depression.
Matching information
This type of question is testing your ability to scan a text and find specific information in it.
The text will have letters identifying each paragraph or section. The question will ask you to find a specific detail in the text. Your answer will be the letter identifying the exact paragraph or section where that specific detail is located. Each paragraph or section may contain several different details so it is possible to use each letter more than once in different questions. The specific detail that you are asked to find could be an example, a reason, a summary, an explanation of something.
It is important to note that this type of question is testing your ability to scan a text backwards and forwards to find information, the order of the questions is not necessarily the order of the information in the text. The order is completely random.
Example:
Questions 22-24
The reading passage has 5 paragraphs, A-E. Which paragraph contains the following information?
Write the correct letter A-E in boxes 22-24
You may use any letter more than once.
22 The location of the new stadium
23 details of how the project has been financed
24 mention of other possible uses of the facilities.
Matching headings
This type of question is testing your ability to identify the main idea of a paragraph or section of the text.
The text itself will have letters (A, B, C etc) identifying each paragraph or section.
On the question sheet, you are given a list of several headings (main ideas), each identified with a Roman numeral (i, ii, iii, etc.)
For each question, you will be given a paragraph letter (A, B, C etc) and you have to choose which of the headings (main ideas) best summarises the contents of that paragraph. Your answer will therefore be a Roman numeral (i, ii, iii, etc.) that you write on the answer sheet.
Note that there are more headings (main ideas) than number of paragraphs. Therefore, some headings will not be used. Each heading or main idea can only describe 1 paragraph.
Example:
Questions 4-7
The reading passage has five paragraphs, A-E.
Choose the correct heading for paragraphs B-E from the list of headings below.
Write the correct number, i-vii, in boxes 4-7
An example is provided.
i A success story
ii Predictions for the future
iii Reasons for the sudden popularity
iv The definition of podcasting
v Necessary equipment to get started
vi Marketing strategies
vii Sources of revenue
Example:
Paragraph A ……….iv……………
4 Paragraph B ……………………
5 Paragraph C ……………………
6 Paragraph D ……………………
7 Paragraph E ……………………
Matching features
You are given a list of numbered statements (each number is the number of the exam question). You are also given a list of options each of which is identified by a letter. For each statement in the question, you have to find the matching option and write its letter on the answer sheet.
Sometimes there will be more options than questions (therefore certain options will not be used.) Sometimes an option may be used more than once. Read the instructions very carefully. The order of the statements in the questions is random. It does not follow the same order as the text. You are being tested on your ability to scan a text and find specific information.
Example:
Questions 4-6
Look at the following statements (Questions 4-6) and the list of people below.
Match each statement with the correct person, A, B, C or D.
Write the correct letter, A, B, C or D in boxes 4-6 on your answer sheet.
4 He realised the speed of a planet going round the sun depends on its distance from the sun.
5 He calculated the distance of the sun from the earth based on onservations of Venus.
6 He understood that the distance of the sun from the Earth could be calculated by comparing observations of a transit.
List of people:
A Johann Franz Encke
B Edmond Halley
C Johannes Kepler
D Guillaume le Gentil
Matching sentence endings
You are given the first part of a sentence. The end of the sentence is missing. You are given a list of possible endings to the sentence, each one identified by a letter (A, B, C etc) You have to choose the correct ending to the sentence based on the text from the passage by writing the relevant letter (A, B, C etc) on the answer sheet. There will be more possible options than questions. Therefore some of the options will not be used.
The order of the questions is the same as the order of the information in the text.
The sentences you are being asked to complete describe main ideas from the text. You are therefore being tested on your ability to understand the main ideas of a text.
Example:
Questions 1-3
Complete the sentences by selecting the correct ending A-E.
1 The first social network intended for college students ………………….
2 By the time facebook launched in 2004, ………………….
3 Aaron Greenspan launched a service that allowed ………………….
A was controversial for how it treated passwords.
B students at Harvard to buy and sell books.
C had begun at Stanford University in 2001
D MySpace had more than a million members.
E to have come up with the idea.
Sentence completion
In this type of question there are several sentences with gaps representing missing words. You will be asked to write the missing word or words. The word limit will be defined in the question. Example: “NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER” – Make sure you read and understand the word limit. You will not be tested on contracted words (example: They’ve) Hyphenated words (example follow-up) count as ONE word. The order of the questions is the same as the order of the information in the text.
Example:
Questions 33-34
Complete the sentences below. Write ONE WORD ONLY for each answer.
33 Mr Graetz says that there is now better co-operation between Australian scientists, government officials and …………………………… .
34 In 1989, Mr Hawke set up Landcare, a …………………………… of regional conservation groups.
Summary, note, table, flow-chart completion
You are presented with a summary of part of the text in 1 of the following formats: Summary (several related sentences), notes (very short related sentences), a table (with rows and columns containing text) or a flow-chart (a chart showing a sequence of events or steps, joined by arrows)
In each format, there are missing words and you have to fill them in. You will either be asked to find the words from the text and fill them in. The word limit will be defined in the question. Example: “NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER”. You will not be tested on contracted words (example: We’re ) Hyphenated words (example pre-defined) count as ONE word.
The order of the answers is random. It is not not necessarily the same order as the words in the passage of text.
Example:
Questions 8-10
Complete the notes below. Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the text for each answer.
New computer system
Compatible with 8…………………………………
Replaces 9…………………………………
Hardware needed 10…………………………………
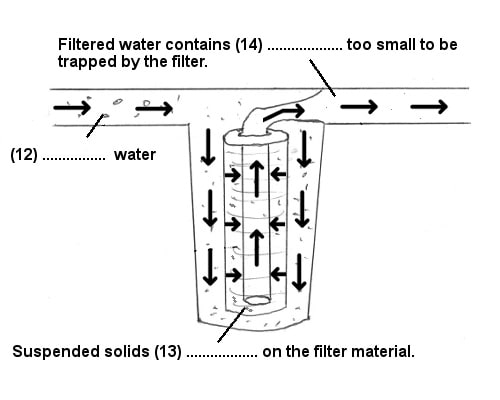
Diagram label completion
You are presented with a diagram which shows some information from the text in picture format. There are labels on the diagram pointing to specific parts of the diagram. The labels have missing words. You are asked to find the missing word or words.
The word limit will be defined in the question. Example: “NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER”. You will not be tested on contracted words (example: We’re ) Hyphenated words (example pre-defined) count as ONE word.
Example:
Questions 12-14
Label the diagram below. Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the text for each answer. Write your answers in boxes 12-14 on the answer sheet.
Short-answer questions
You are asked a question related to the reading text. You are asked to write the answer as a word or several words. The word limit is defined in the question. Example: “NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER” – It’s therefore very important to read the instructions carefully and understand the word limit. You will not be tested on contracted words (example: I’ll) Hyphenated words (example pre-meditated) count as ONE word.
Example:
Questions 31-32
Answer the questions below. Choose NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS from the text for each answer.
31 How did the football team travel to London?
32 What did the manager find on his desk?
IELTS writing
The IELTS writing exam lasts for 60 minutes. There are 2 questions or tasks – Task 1 and task 2.
Task 1 answers are marked on the following 4 criteria:
Task achievement
Coherence and cohesion
Lexical resource
Grammatical range and accuracy.
Task 2 answers are marked on the following 4 criteria:
Task response
Coherence and cohesion
Lexical resource
Grammatical range and accuracy.
The type of question asked in task 1 and 2 depends on whether the candidate is taking the IELTS Academic or the IELTS General Training exam.
IELTS Academic writing
You must complete 2 tasks as follows:
Task 1: You are asked to describe a visual graph, table, chart or diagram in your own words. The word limit is a minimum of 150 words in 20 minutes.
Task 2: You are asked to write an essay in an academic style about a given topic. The word limit is a minimum of 250 words in 40 minutes.
IELTS General Training writing
You must complete 2 tasks as follows:
Task 1: You are given a situation and context and then asked to write a letter to respond to that situation. The situation is usually an everyday situation such as asking for more information about something or complaining about bad service. The style required (formal or informal) for the letter will depend on the given situation. The word limit is a minimum of 150 words in 20 minutes.
Task 2: You are asked to write an essay about a given topic. The topic is often of general interest and related to an aspect of society. The word limit is a minimum of 250 words in 40 minutes.



Nworgu chioma says
Please, I don’t understand what u mean by ‘ not more than three words and/ or a number’.